African Pied Wagtail
Motacilla aguimp - Bergeronnette pie
Identification
The African Pied Wagtail is a medium-sized bird, 20 cm, with two predominant colors on its entire body. The head is black with a very wide white eyebrow extending from the lores to the nape. The throat is white. A broad black breast band shaped like a bib can go down to the chest. Narrower on the sides, it reveals two white spots on either side of the neck. The flanks and the belly are white. The mantle, the scapulars and the back are black. The rump is gray-black. The flight feathers are black with white outer edges when the wings are closed. In flight, the two colors are well distinguished. The tips of the primary and secondary remiges are black, the median and small coverts are white and the tectrices are black. The central rectrices are black surrounded by two pairs of white feathers. The iris is brown, the bill is dark and the feet are black. Only a difference in intensity in the dark parts can distinguish the two sexes. In inter-nuptial plumage, the male is rather slate gray on the back. The female has less intense colors that become dark olive gray in inter-nuptial plumage. The immature has the dark plumage of the adult but is brown-olive in colour, the white parts are rather dirty white.
Subspecific information 2 subspecies
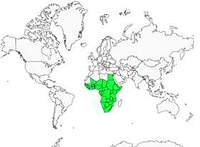
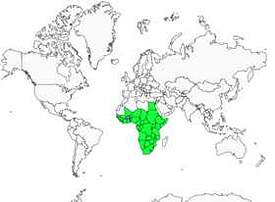
- Motacilla aguimp aguimp (s Namibia to c South Africa)
- Motacilla aguimp vidua (Sierra Leone and Mali to s Sudan and nw Kenya, s Egypt to s Somalia and south to e South Africa)
Foreign names
- Bergeronnette pie,
- Lavandera africana,
- alvéola-pretibranca,
- Witwenstelze,
- özvegybillegető,
- Afrikaanse Bonte Kwikstaart,
- Ballerina nera africana,
- brokärla,
- Afrikaerle,
- trasochvost africký,
- konipas africký,
- Afrikansk Vipstjert,
- afrikanvästäräkki,
- Bontkwikkie,
- cuereta africana,
- Árerla,
- pliszka srokata,
- Āfrikas cielava,
- deviška pastirica,
- Пегая трясогузка,
- ハジロハクセキレイ,
- 非洲斑鹡鸰,
- brokärla,
- 非洲斑鶺鴒,
Voice song and call
The song of the African Pied Wagtail is melodious and sustained by whirring notes weet-weet, wip-wip-wip, weet, wee-wee repeated several times. It easily mimicks the Garden Bulbul and the Bush-warbler. It can call in the following ways: tweet sharp or chizzit, quick-quick-treeet, wee-wee-wee or tseet-tseet-tseet with the final note higher than the rest of the phrase.
Habitat
The African Pied Wagtail lives in wet, tropical regions of Southern Africa. It breeds near human dwellings, farms or villages. It is common on roofs and roads in cities, lawns, parks and gardens. It can also be found in reservoirs and dams, on lakes, coastal lagoons, ponds and sandy banks or rocky areas along rivers and streams. In drier regions, it stays near rivers. It can be seen from sea level to 3000 metres altitude in East Africa.
Behaviour character trait
African Pied Wagtail is a monogamous species usually seen in couples or in small family groups with herds of herbivores.
Outside of the breeding season, the groupings can reach up to one hundred individuals. They are gathered around zones of preferred feeding. Groups feed nearby each other. Territorial, the African Pied Wagtail will chase off any intruder outside of its territory. With each season, breeding couples have multiple broods. Usually up to three broods per season, even up to seven in Kenya, are counted. African Pied Wagtail walks and hops. It hunts its prey on the ground and in the air. Once caught, it will seclude itself in a quiet place to kill and tear into small pieces before swallowing them.Dietfeeding habits
The African Pied Wagtail is mainly insectivorous. It feeds on the ground, walking and jumping, invertebrates and their larvae: butterflies, dragonflies, grasshoppers, flies and ants. Seeds, tadpoles, small fish and human food leftovers are added to its diet. It is not uncommon to see it flying over the water to capture insects close to the surface.
Reproduction nesting
The African Pied Wagtail's nest, built by both sexes, consists of dried grasses which form a cup. Bad weeds, roots, stems, leaves, straws, vegetable debris and strings are among the materials gathered for its construction.
The inside of the cup is lined with rootlets, feathers and fine grasses. It is usually placed near water or close by vegetation, for example in reed beds. Artificial sites such as holes in walls, building edges, bridges, roofs and boats are commonly used as well. The female lays 2 to 5 white eggs almost all year round, with two peaks corresponding to the period before the rains, from August to November and from February to April. Despite the female incubating mainly, the male partakes in the incubation which lasts between 12 and 15 days. The nestlings are fed by both parents who give preference to insects. They take flight between 15 and 18 days from birth, and remain dependent on the adults for about two weeks. Finally, they are forced out of the territory just before the next clutch. The nest is parasitised by the Eurasian Wood-Cuckoo, the Long-tailed Cuckoo and the Jacobin Cuckoo.Threats - protection
IUCN conservation status
concern
in the Wild
threatened
evaluated
The species is not generally threatened although locally its population may have slightly decreased. It is closely associated with humans and has been able to benefit from the building of many dams.
Sources of information
- IOC World Bird List (v15.1), Gill, F and D Donsker (Eds). 2025-12-07.
- HBW Alive,
- Birds of Southern Africa, Tony Roocroft
- Biodiversity explorer The web of life in Southern Africa,
Other sources of interest
 Specification sheet created on
22/07/2023 by Nathalie Santa Maria
Specification sheet created on
22/07/2023 by Nathalie Santa MariaTranslation by AI Oiseaux.net
© 1996-2026 Oiseaux.net
- Accipitriformes
- Aegotheliformes
- Anseriformes
- Apodiformes
- Apterygiformes
- Bucerotiformes
- Caprimulgiformes
- Cariamiformes
- Casuariiformes
- Charadriiformes
- Ciconiiformes
- Coliiformes
- Columbiformes
- Coraciiformes
- Cuculiformes
- Eurypygiformes
- Falconiformes
- Galliformes
- Gaviiformes
- Gruiformes
- Leptosomiformes
- Mesitornithiformes
- Musophagiformes
- Nyctibiiformes
- Opisthocomiformes
- Otidiformes
- Passeriformes
- Pelecaniformes
- Phaethontiformes
- Phoenicopteriformes
- Piciformes
- Podargiformes
- Podicipediformes
- Procellariiformes
- Psittaciformes
- Pterocliformes
- Rheiformes
- Sphenisciformes
- Steatornithiformes
- Strigiformes
- Struthioniformes
- Suliformes
- Tinamiformes
- Trogoniformes